Table of contents
- Volume
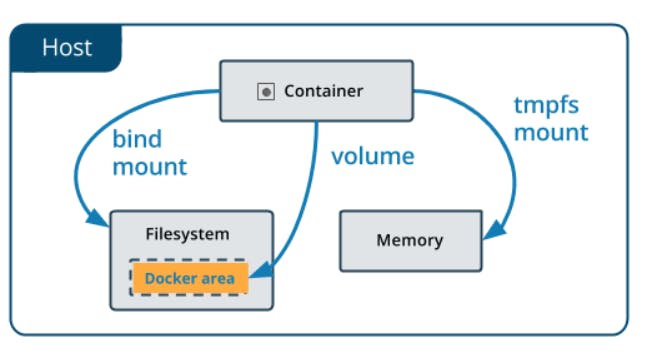
- Docker has two options for containers to store files in the host machine so that the files are persisted even after the container stops:
- Step for Install Docker in Ubuntu
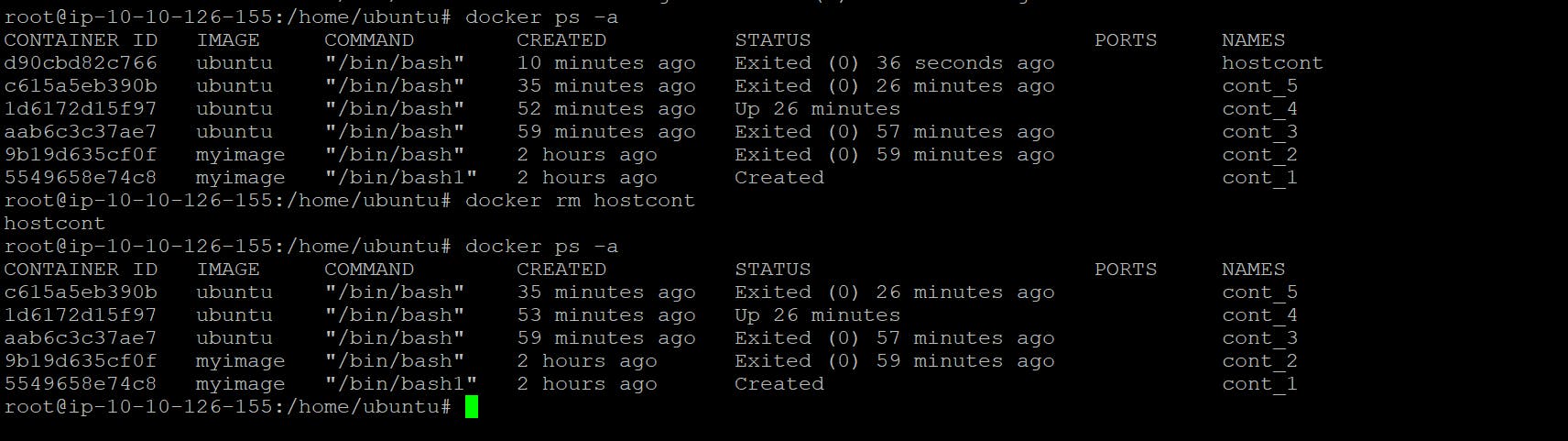
- To Delete Container
- To Create a Conatiner
- To Check Volumes
- Steps For Creating Volume
- Volume by command and shared between Two Container
- Shared volume by host to container
- ThanK You
Volume
Volumes are the preferred mechanism for persisting data generated by and used by Docker containers. While bind mounts are dependent on the directory structure and OS of the host machine, volumes are completely managed by Docker. Volumes have several advantages over bind mounts:
Volumes are easier to back up or migrate than bind mounts.
You can manage volumes using Docker CLI commands or the Docker API.
Volumes work on both Linux and Windows containers.
Volumes can be more safely shared among multiple containers.
Volume drivers let you store volumes on remote hosts or cloud providers, to encrypt the contents of volumes, or to add other functionality.
New volumes can have their content pre-populated by a container.
Volumes on Docker Desktop have much higher performance than bind mounts from Mac and Windows hosts.
Docker has two options for containers to store files in the host machine so that the files are persisted even after the container stops:
Volumes are stored in a part of the host filesystem, which is managed by
Bind mountsmay be stored anywhere on the host system.
Step for Install Docker in Ubuntu
1. update the local system
apt-get update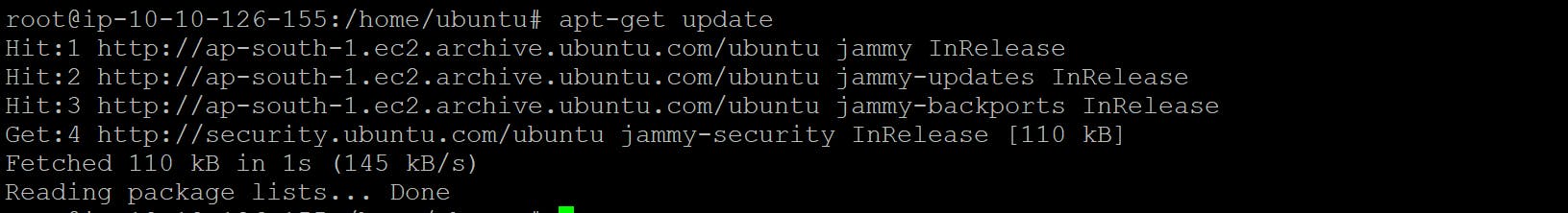
2. Now Install Docker
apt-get install docker.io -y
3. Now Check Docker Status
service docker status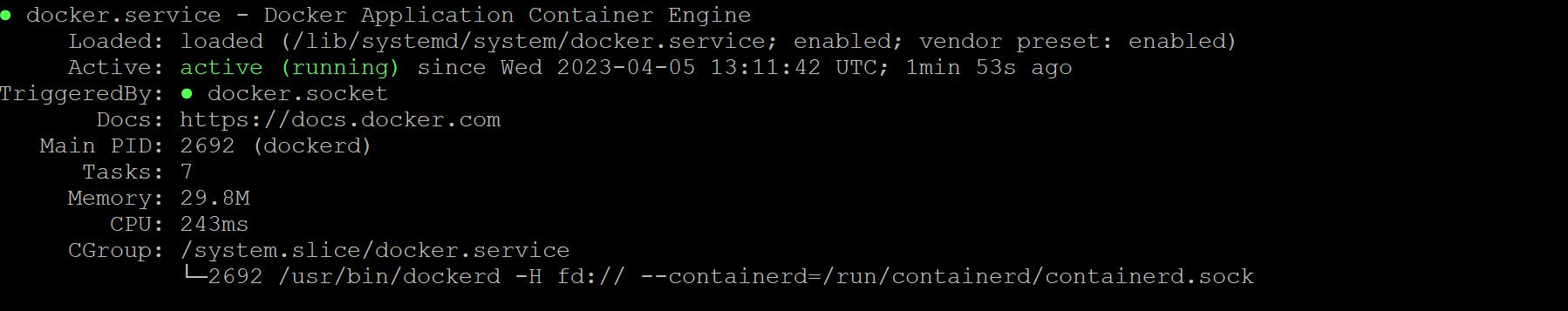
To Delete Container
docker rm <container_name>
To Create a Conatiner
docker volume create <volume_name>
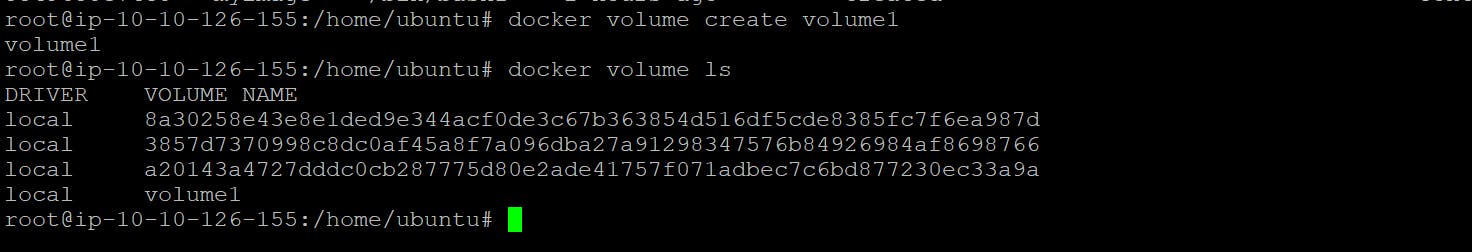
To Check Volumes
docker voolume ls

Steps For Creating Volume
Volume by Docker File
Volume by command and shared between two container
Shared volume by host to container
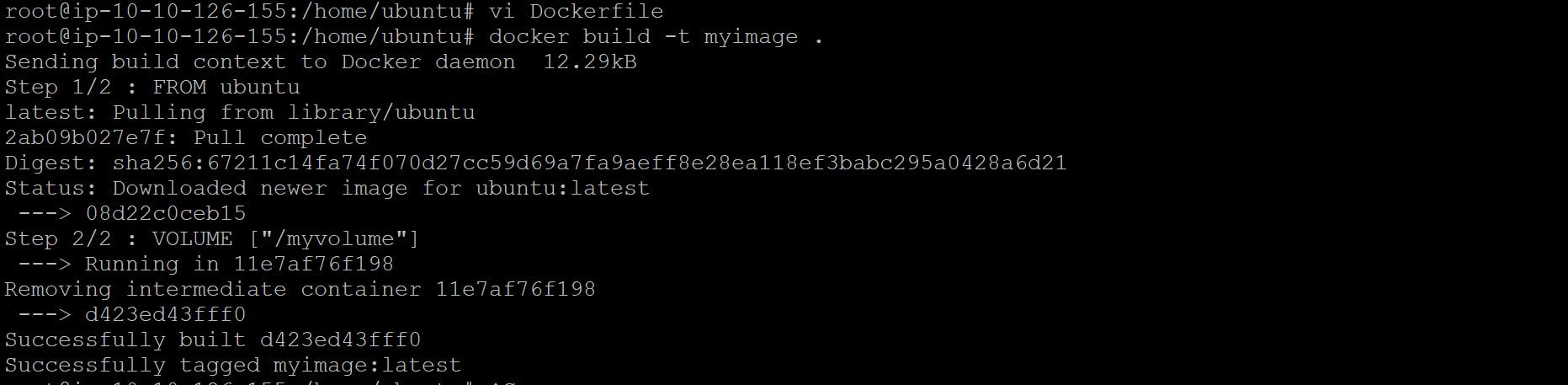
Volume by Docker File
creating file Docker name ex vi Dokcerfile

Now create image from Docker file
docker build -t <image_name>
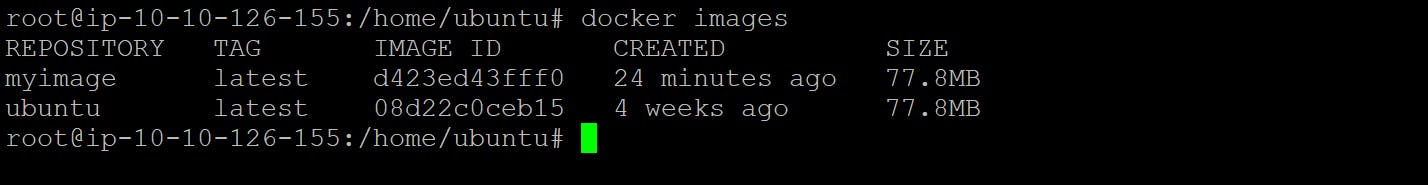
Now Check Image create or Not
docker images
Now create Container from that Images
Docker run -it --name <container_name> <image_name> /bin/bash

now check container
docker ps -a

Now start the container
docker start <container_id>

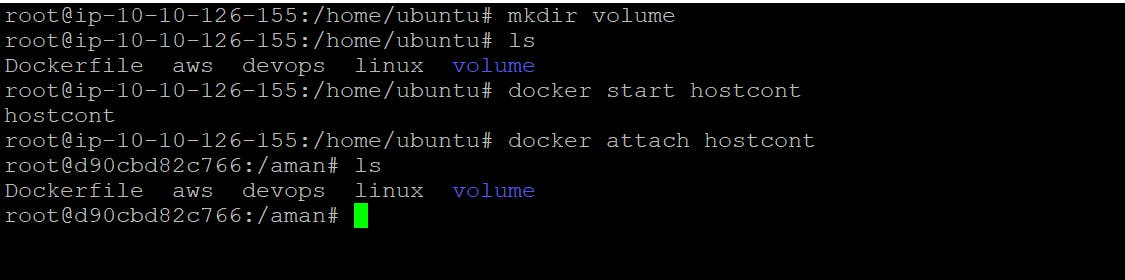
Now go inside the container
docker attach <container_id>

now create some file in myvolume and exit from conatiner
touch filex filey filez

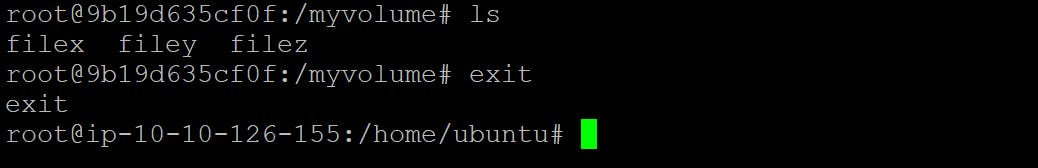
Now create new continer from update container
docker run -it --name cont_2 --privileged=true --volumes-from cont_1 ubuntu /bin/bash

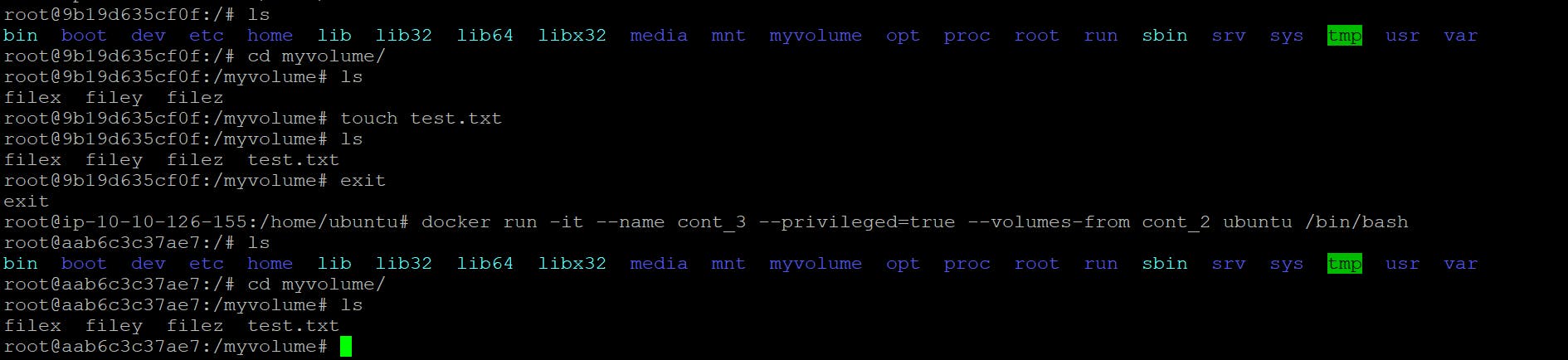
so here container is created and volume ""myvolume"" is attach is both container all th3 files are there.
Volume by command and shared between Two Container
docker run -it --name <continer_name> -v /<vomlumename> <image_name> /bin/bash
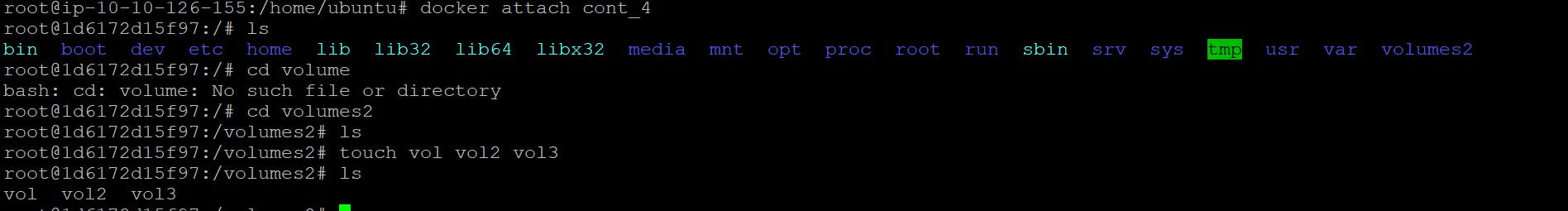
now create another container from update container
docker run -it --name <container_name> --privileged=true --volumes-from <container_name> <image_name> /bin/bash
Now We added some file is this container and check on con_4 file automated added or no in volumes

Now Created some file in con_3 and exit from cont_3

Now Start and Attach the Container_4 and see that changes
docker start <container_id> docker attach <container_id>
Now see the Change here volume is shared in each container once we update in any file its automatically updated in both volumes of both container

Shared volume by host to container
create a 3 fileson your local system
touch devops aws linux
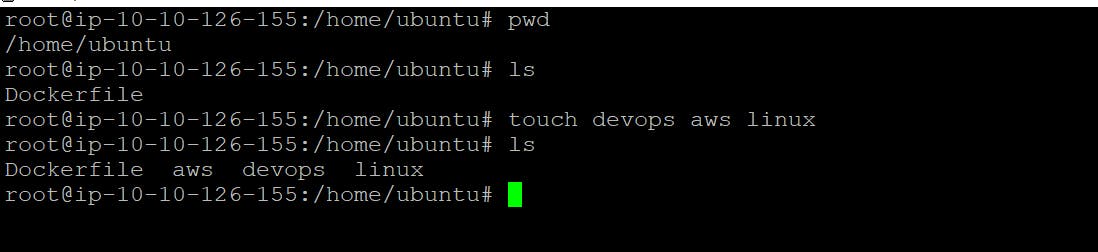
Now Create Conatiner at local Ubuntu
docker run -it --name <container_name> -v /home/ubuntu:/<volume_name> --privileged=true <image_name> /bin/bash
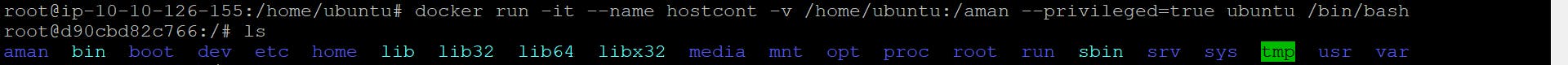
Now Volume is Created and all the file are in Local Ubuntu are shared with Hostvolume

Now Update on Host-Volume and see the change is Aman